ORA Pro - 社会网络分析工具
ORA Pro是一个用于网络分析,网络可视化和网络预测的工具。这个软件工具使用户能够分析动态元网络并处理非常大的数据集。ORA可以处理一百万个(或以上)节点。它使用图形、统计和可视化帮助用户输入、分析、可视化和预测网络中的变化。ORA是为支持对高维网络的分析,这些网络包括可以随时间变化的关系和可能位于地理-时间位置的关系;即动态meta-networks。使用ORA软件,可以评估谁、什么、在哪里、什么时候、如何以及为什么日常生活中的多重价值关系。
WHAT IS ORA?
ORA is network analysis and visualization software package that helps the user enter, analyze, visualize, and forecast changes in networks using graph, statistical and visualization based techniques. ORA is designed to support the analysis of high dimensionality networks that include relationships that can change through time and that may be geo-temporally located; i.e. dynamic mata-networks. Using ORA, multiple valued relationships among the who, what, where, when, how and why of everyday life can be assessed.
WHAT SIZE OF NETWORKS?
ORA supports the analysis of networks ranging in size from only a few nodes (e.g. 2) to approximately 15 million nodes per node-class. The size of the networks that can be processed depends on: 1) the memory and number of cores on the machine being used; 2) whether or not you are using the basic version of ORA or the batch version; 3) the number of attributes and the kinds of attributes per node (e.g. attaching images, icons, urls, and full texts to nades decreases the number of nodes that can be handled); and 4) the number of node-classes(yes there is a size per class versus number of classes tradeoff).
WHAT KIND OF NETWORKS CAN BE ANALYZED?
Any thing that can be represented as nodes and relations can be analyzed in ORA. A common type of network is the social network where the nodes represent agents, generally people or organizations, and the links represent a type of relationships such as friendships, works together, or mentors. A key feature of ORA is that the networks are organized into meta-networks.
A meta-networks is a collection of inter-related networks and the associated node and link attributes for a specific time period. Meta-networks are composed of a set of node-classes, and networks. Each node-class contains a set of nodes of a particular type. The types used by ORA are agents, organizations, knowledge, resources, tasks, evevts, beliefs, and locations.
A network is a collection of relations of one type between nodes within one or two node-classes. If there are two relations between the same set of nodes, you would create two networks-e.g. friendship and mentoring would each be their own network within the same meta-network between agents.
For over time data a set of meta-networks are used. These can be included in ORA as either discreet networks one per time period, or as "delta" on the prior meta-network.
HOW IS ORA ORGANIZED?
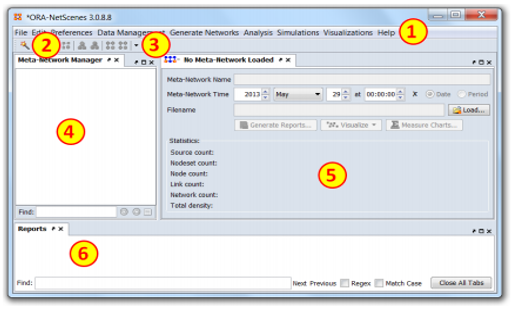
ORA consists of 5 main components:
1. The Importer, which allows you to enter data from a variety of formats, such as from excel. This includes importing data from many of the formats in which other tools export network data.
2. The Editor, which allows you to edit the nodes and relations within and across networks. This include the ability to add, delete and merge nodes, move nodes between node classes, change the values of relations, and add or delete attributes of nodes. Note, the editor can by itself be used to enter data!
3. The Data Manager, wnich allows you to manipulate networks. This include the application of standard matrix algebra techniques as well as applying special functions across multiple networks.
4. The Reports, which allows you to assess and evaluate the networks from both a standard social network perspective and the more highly dimensional meta-network perspective used in dynamic network analysis. Each report addresses a network question and automatically calculates for the user the relevant available metrics. The results of the analysis with simple descriptions of the meaning of those results are provided.
5. The Visualizers, which allow you to visually manipulate networks and identify important results such as key actors, groups, and spatial or temporal trends, There are multiple visualizers including 2D graphs, 3D graphs, geo-spatial, trails (space and time), nodel (Word Cloud for nodes), and assorted graphing techniques.
- 2026-02-09
- 2026-01-20
- 2026-01-16
- 2026-01-12
- 2026-01-12
- 2026-01-09
- 2026-02-26
- 2026-02-26
- 2026-02-26
- 2026-02-11
- 2026-02-05
- 2026-02-05